Lumbar Disc Herniation Specialist
A lumbar disc herniation occurs when the spinal disc bulges or ruptures into the spinal cord causing nerve irritation. Most patients benefit from conservative therapies, however, surgical intervention may be necessary for severe cases. Doctor Andre M. Samuel, orthopedic spine specialist offers both surgical and non-surgical treatment options for patients in Clear Lake, Houston, and Sugar Land, Texas area, who are experiencing a lumbar disc herniation. Contact Dr. Samuel’s team today!

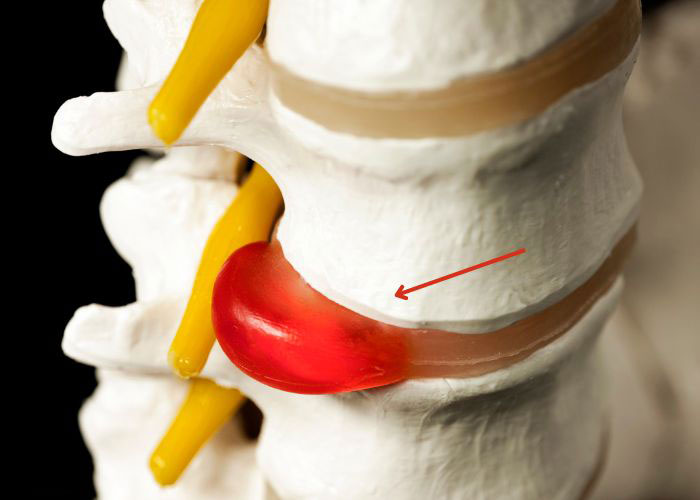
What is a lumbar disc herniation?
The last five vertebrae of the spinal column is the lumbar spine. Between these vertebrae is a tough and rubbery disc that reduces friction by acting as a shock absorber. The contents of this intervertebral disc can protrude against its outer shell and into the spinal canal causing mechanical compression of the spinal nerves. A lumbar disc herniation can be the result of the natural aging process or from a sudden and traumatic injury such as a fall. If the pressure on the lumbar intervertebral disc continues, the jelly-like contents may rupture through the disc’s outer ring releasing chemical irritants that can add to the already present nerve inflammation. Dr. Andre M. Samuel, orthopedic spinal specialist serving Sugar Land, Pearland, and the Houston, Texas area, has the knowledge and understanding, as well as substantial experience, in treating patients who have experienced a lumbar disc herniation.
Are there risk factors for a lumbar disc herniation?
Yes. There are a number of factors that can increase an individuals’ risk of developing a lumbar disc herniation. These include but are not limited to:
- Men are more likely to develop a herniated disc between 20 and 50 years old.
- Weight/Body Mass. Individuals who are overweight place additional stress onto the lower back.
- Lifting Techniques. Lifting heavy objects with the lower back muscles instead of the leg muscles can cause a lumbar disc herniation. Twisting while lifting these objects can also cause unnecessary pressure on the intervertebral discs.
- Sedentary Lifestyle. Sitting for long periods of time with no regular exercise can make an individual more susceptible to a lumbar disc herniation.
- Tobacco Use. Smoking has been found to cause early disc degeneration due to the lack of oxygen supply.
- Occupational/Recreational Hazards. Some jobs and recreational activities can be physically demanding with constant lifting, pushing, pulling, and twisting movements.
- Long periods of time in a seated position in addition to the car engine’s vibration can add pressure to the lower back.
What are the symptoms of a lumbar disc herniation?
The first and most common symptom of a lumbar disc herniation is low back pain. Some other common symptoms of a lumbar disc herniation include:
- A sharp and shooting pain from the buttocks down the back of one leg, also called sciatica
- Decreased sensation
- Muscle spasms
- Loss of lower extremity muscle strength
- Numbness and/or tingling sensation of the lower extremity and possibly the foot
- Loss of bladder or bowel control; a rare symptom that requires immediate medical attention
How is a lumbar disc herniation diagnosed?
Dr. Samuel will first gather a thorough medical history and then perform a physical and neurological examination to diagnose a lumbar disc herniation. The lower back, abdomen, and lower extremities are evaluated for any signs of decreased sensation, muscle weakness, or abnormalities in the nerve reflexes. Diagnostic imaging studies, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), can further delineate the affected lumbar intervertebral disc.
What is the treatment for a lumbar disc herniation?
Non-surgical treatment:
Patients with a lumbar disc herniation often respond well to conservative treatment options. These individuals report symptom improvement or complete resolution in 3 to 4 months with consistent treatment measures. Short periods of bed rest in addition to activity modifications can help alleviate any symptoms. To reduce pain and swelling of the lower back, Dr. Samuel recommends non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs). An epidural steroid injection may be administered near the irritated nerve root to calm the inflammation and pain. Specific exercises targeting the lower back and abdomen can help strengthen these muscles to prevent re-injury.
Surgical treatment:
A small number of individuals require surgical intervention for a lumbar disc herniation. Surgical candidates are patients who trialed conservative therapies with little to no symptom improvement. A lumbar disc herniation is surgically corrected by removing all or part of the damaged intervertebral disc through a small incision. Advancements in technology have improved these surgical procedures and created different techniques for surgeons to utilize based on patient-specific factors. Dr. Samuel will determine the best surgical approach based on the severity of the lumbar disc herniation and the location of the affected nerve root.


